Multi Factor Authentication (MFA), is the process of confirming a user’s identity with the use of two or more security mechanisms (factors). Only after all pieces of evidence have been successfully confirmed, access to the user is granted.
Using multi-factor authentication provides a secure authentication mechanism that is not the primary target of brute force attacks as traditional single-factor methods like username/password combinations.
Single-factor authentication methods have been used for decades, but are becoming less secure with the increase of phishing attacks and other online threats. Authentication methods that use more than one factor are more secure because if any one of the factors is compromised by an attacker, the attacker will still be required to provide at least one more piece of evidence before they can be authenticated. Since a thief or hacker isn’t likely to obtain both the password and the token, user authentication becomes more secure and less susceptible to hijacking or guessing.
Multi-factor authentication continues to grow more urgent as attackers find ways to break into accounts that use single factor methods such as user passwords. MFA protects users who click on links in untrusted emails by requesting additional authentication before they can give out sensitive information via increasing phishing schemes. It prevents users from sharing passwords, which creates a lot of risk and can cause financial losses if the attacker installs ransomware in their systems.
Multi-factor authentication includes verification technologies from three different groups, such as
- Knowledge (something the user and only the user knows)
- Possession (something the user and only the user has)
- Inherence (something the user and only the user is)
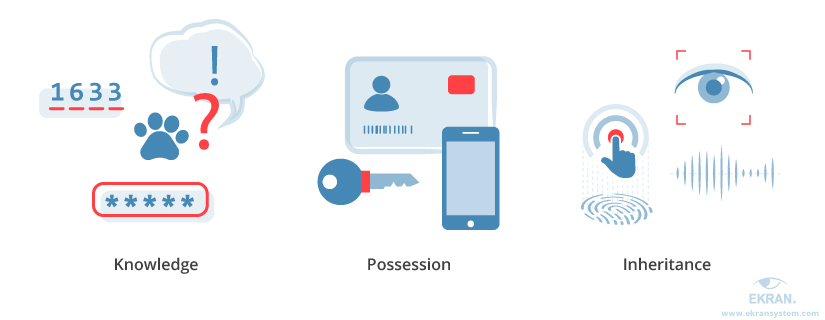
Knowledge is usually a password, PIN, passphrase or questions and their corresponding answers. In order to satisfy this technology, the user must enter information that the backend can then match against that which has been previously setup or stored.
Possession include tokens or smart cards. Smart cards are small, easy-to-use hardware devices that an owner carries with them to authorize access to a network service. Supporting strong authentication with one-time passwords (OTPs), these hardware tokens provide the possession factor for multi-factor authentication while enabling enhanced security for banks and application providers who need to secure multiple applications with a single device. Today, most users use their smartphone as the device that generates these authentication tokens or allows them to respond back to a server with a one-time use code behind the scenes.
Inherence is anything from fingerprints, retina scans, facial recognition, voice recognition, or a user’s behavior (such as how hard or fast they type or swipe on a screen) that can be used to identify a unique user. This includes using fingerprint scans or face recognition in order to authenticate users.
Another type that is not very common is context, which is a physical location or IP address that only the user can verify.
Contextual factors include the user’s geo location, the time they authenticated, and their device’s IP address. Context-based authentication adds a user’s whereabouts (with the time and the IP address or device they are using). This helps banks prevent unauthorized access if someone tries to access an ATM from two different countries within a short period of time. If this happens, the bank can lock the user’s access until they use other methods of authentication. Also, since users typically carry their smartphones and most, if not all smartphones have a GPS device, it becomes easier to confirm the user’s identity using this authentication method.
To achieve multi-factor authentication, at least two methods from at least two different technology groups must be used. As a result, using a PIN coupled with a password would not be considered multi-factor authentication, while using a PIN with facial recognition would be.
Multi-factor authentication should be used when accessing any sensitive data, such as a bank account at an ATM, which requires two methods of verification, including something the user knows (the PIN), and something the user has (the ATM Card).
Banks and other financial websites usually offer multi-factor authentication as a default, so users should take advantage of it in order to keep their information more secure. Biometric authentication methods, like face recognition are regarded as very secure and are used in places where it’s critical to keep unauthorized personnel out of secure areas. Biometrics are not very efficient for online transactions or ATMs due to high cost required for hardware as well as user acceptance. Most users prefer not to have their face scanned when doing things like ATM transactions. As an alternative, banks and corporations are making use of tokens as a mean of two-factor authentication.
With the current wave of phishing attacks, it’s really important to validate and control access. This is one of the main reasons multi-factor authentication should be a requirement in any company, especially if they need to protect sensitive data. With cyber security in the rise in recent years, IT departments have had to learn better ways to keep attackers out of their systems. Also, since a lot of companies have migrated their data and applications to the cloud, it is becoming even more critical to design and implement better security plans that use multi factor authentication.
Single factor authentication, such as passwords, are recognized to be one of the easiest for hackers to bypass. Therefore, most companies should implement MFA strategies to defend or secure their clients and users. Implementing multi factor authentication methods will help companies secure their valuable data by making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access. To keep data as secure as possible, employees should use a mixture of authenticating factors like hardware, software, and SMS tokens when requesting access.
While MFA is more secure than single or two factor authentication, it’s also more difficult to implement without affecting users efficiency. Sometimes users are slowed down because of the extra effort it takes to provide multiple methods of authorization in order to access their data. Other disadvantages of using smart cards is when unexpected events occur, like forgetting the device at home, can cause the users to get unauthorized access. Implementing multi-factor authentication can also be an inconvenience to the users, given that there are at least three possible factors in MFA.
Companies are looking to have far more granular control over their users’ authentication without affecting their workflow. What should also be considered when deciding on an authentication method, is that attackers will spend a lot of time and resource into trying to find ways to compromise credentials. Therefore, companies must not only control access, but train users so they are aware of phishing attacks. They should also monitor what users are doing with their access, looking for abnormal patterns by looking at system logs in order to determine if an attacker has gained access. The training, along with system monitoring provides the possibility of preventing unauthorized access from compromised credentials.
In order to design a proper MFA process, there should be a balance between security and user experience. If the process leans too far to either side, it will create an imbalance, which can negatively impact the users. Just like all security processes, multi-factor authentication does not guarantee that an attacker will not gain access to a company’s systems. It is critical to understand the pros and cons of using MFA before designing security procedures. Knowing the risks and limitations of MFA is the first step towards better overall security.
Summary
If you work as a systems admin and haven’t yet implemented MFA at work, then it’s time to implement it before it’s too late. Many companies are falling for phishing attacks and usually what follows is a ransomware attack.
If you don’t work in the tech industry, you should still implement this on your online accounts. There are many apps that offer MFA, but I recommend Microsoft Authenticator. I have been using it for the past few years and it works great.
If you enjoyed this post, I would appreciate a follow on Twitter at hsantoyo_sec. I’m currently working on a SaaS startup and would like to get an audience in the tech and startup space.